hydrogen
What IS hydrogen?
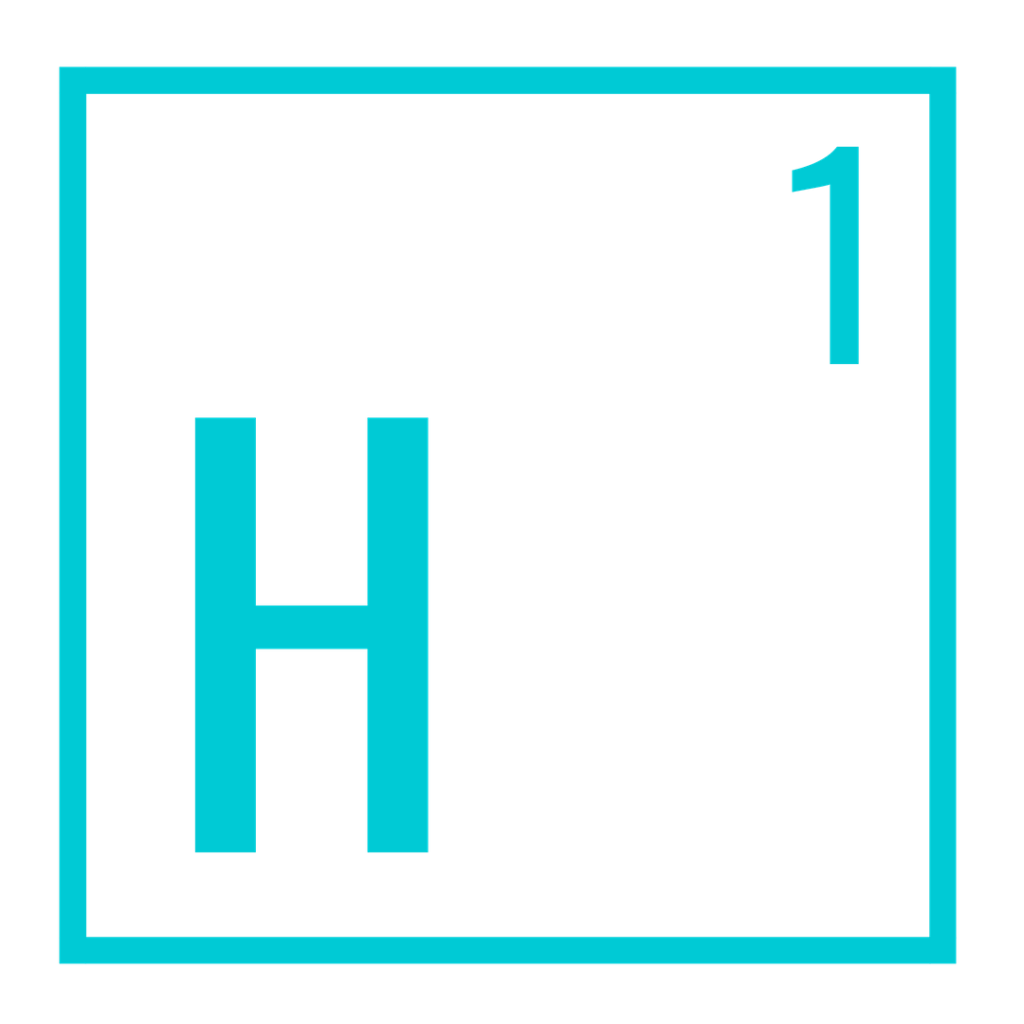
Hydrogen atomic weight: 1.00794 Diatomic weight: 2.016 Size: 50-53 (pm) (pico-meters, 1/trillionth of a meter) Density: 0.0899 g/L Melting point: (- 434.45 °F), (-259.14 °C) Boling point: (- 423.17 °F), (- 252.87 °C) Form at room temperature: Gas
Hydrogen is number one on the periodic scale and is the smallest and lightest element in the universe.
Percentages based on mass:
- Universe: 75%
- Earth crust: 0.15 %
- Ocean: 11%
- Human body: 10%
Hydrogen Facts:
- The most abundant element
- Constitutes 75% of the universe
- Smallest and lightest atom, with one proton and one electron, making it first on the periodic table
- Virtually every other element derived from Hydrogen
- Can exist in the form of gas, liquid, and a recently discovered metallic state
- Mostly found on earth in the form of water (H2O) and in the form of organic compounds
- An essential element for life and plays a vital role in the human body
- Exists in most organic molecules
- The central point of the acid-base reactions
Molecular Hydrogen Facts:
- Two hydrogen atoms, covalently bonded together (sharing electrons)
- Neutral in charge
- Lighter than air itself
- Colorless, odorless, tasteless, flammable, diatomic gas
- Flammable between 4%-75%, except when dissolved in water
- A clean energy source; 3 times more energy dense than gasoline
- Has been used in fuel cell technology, agriculture, etc
- It was not until the 21st century that it was discovered to potential have remarkable therapeutic benefits to the human body
- Multiple therapeutic functions, some of which are still being discovered.
- Now being recognized as a medical gas exerting antioxidant effects, anti-inflammatory effects, anti-cellular death effects, etc.